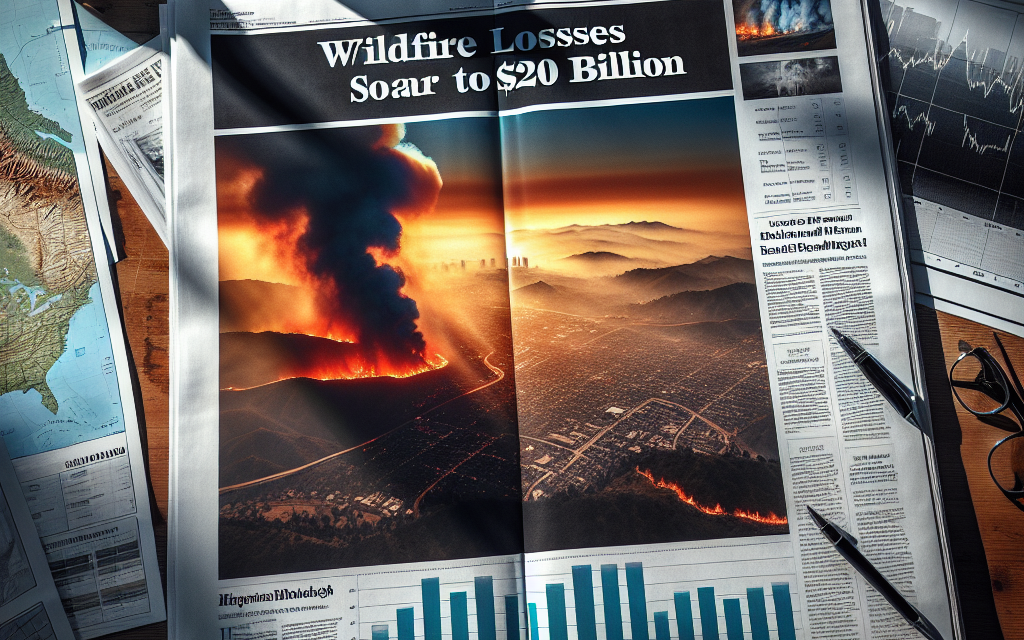
“US Insurers Reeling as Los Angeles Wildfire Losses Surge to $20 Billion.”
Introduction
The recent surge in wildfire losses in Los Angeles has posed a significant challenge for U.S. insurers, with damages soaring to an estimated $20 billion. This unprecedented financial impact highlights the growing risks associated with climate change and the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires in California. Insurers are now grappling with the implications of these losses on their operations, pricing strategies, and overall market stability. As they navigate this crisis, the industry faces critical questions about risk assessment, policy coverage, and the sustainability of insurance models in the face of escalating natural disasters.
Insurer Financial Impact of Los Angeles Wildfires
The recent wildfires in Los Angeles have resulted in staggering financial repercussions for insurers, with losses soaring to an estimated $20 billion. This unprecedented figure not only highlights the severity of the wildfires but also underscores the growing challenges faced by the insurance industry in managing risks associated with climate change and natural disasters. As the frequency and intensity of wildfires increase, insurers are grappling with the implications of these catastrophic events on their financial stability and operational strategies.
In the wake of the Los Angeles wildfires, insurers are confronted with a surge in claims that far exceeds initial projections. The sheer scale of destruction, which has affected thousands of homes and businesses, has led to a significant uptick in payouts. This situation is exacerbated by the rising costs of rebuilding and repairing properties, as inflation and supply chain disruptions further inflate expenses. Consequently, insurers are compelled to reassess their risk models and pricing strategies to ensure they remain solvent in the face of such overwhelming losses.
Moreover, the financial impact of the wildfires extends beyond immediate claims. Insurers are also facing increased reinsurance costs, as reinsurers adjust their pricing in response to the heightened risk environment. This adjustment can lead to a cascading effect, where primary insurers pass on these costs to policyholders through higher premiums. As a result, consumers may find themselves facing steeper insurance rates, which could lead to a decrease in coverage as individuals and businesses seek to cut costs. This trend raises concerns about the affordability and accessibility of insurance in high-risk areas, potentially leaving many without adequate protection against future disasters.
In addition to the direct financial implications, the wildfires have prompted insurers to reevaluate their underwriting practices. Insurers are increasingly adopting more stringent criteria for policy issuance, particularly in regions prone to wildfires. This shift may result in a tightening of coverage options, as insurers become more selective about the risks they are willing to underwrite. Consequently, homeowners and businesses in fire-prone areas may struggle to secure insurance, leading to a potential insurance gap that could leave them vulnerable in the event of future disasters.
Furthermore, the wildfires have sparked discussions about the need for innovative solutions within the insurance industry. As traditional models face mounting pressure, there is a growing recognition of the importance of integrating technology and data analytics into risk assessment and management. By leveraging advanced modeling techniques and real-time data, insurers can better understand and predict the risks associated with wildfires, allowing them to make more informed decisions regarding coverage and pricing.
In conclusion, the financial impact of the Los Angeles wildfires on insurers is profound and multifaceted. With losses reaching $20 billion, the industry is at a critical juncture, facing challenges that necessitate a reevaluation of risk management strategies and underwriting practices. As insurers navigate this complex landscape, the need for innovative approaches and a commitment to sustainability will be paramount. Ultimately, the lessons learned from these devastating wildfires may shape the future of the insurance industry, prompting a shift towards more resilient and adaptive practices that can better withstand the realities of a changing climate.
Rising Insurance Premiums in California
As the devastating impact of wildfires continues to unfold in California, the insurance landscape is undergoing significant changes, particularly in the wake of the recent Los Angeles wildfire losses, which have soared to an alarming $20 billion. This staggering figure not only highlights the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires but also underscores the broader implications for insurance premiums across the state. In response to these catastrophic events, insurers are compelled to reassess their risk models, leading to a notable rise in insurance premiums for homeowners and businesses alike.
The correlation between wildfire losses and rising insurance premiums is becoming increasingly evident. Insurers, faced with mounting claims and the financial strain of covering extensive damages, are adjusting their pricing strategies to mitigate future risks. Consequently, many policyholders are experiencing significant increases in their premiums, which can be particularly burdensome for those already grappling with the economic fallout of natural disasters. This trend is not isolated to Los Angeles; rather, it reflects a statewide phenomenon as California grapples with the realities of climate change and its associated risks.
Moreover, the rising premiums are not merely a reflection of immediate losses but also a response to the long-term outlook for wildfire risks in California. As climate models predict more frequent and severe wildfires, insurers are increasingly wary of the potential for future losses. This heightened awareness is prompting companies to implement stricter underwriting criteria, which can further exacerbate the challenges faced by homeowners seeking coverage. In many cases, individuals in high-risk areas may find it increasingly difficult to secure affordable insurance, leading to a growing sense of insecurity regarding property protection.
In addition to the direct impact on premiums, the rising costs of insurance are also influencing the real estate market in California. Prospective homebuyers are becoming more cautious, weighing the potential costs of insurance against the backdrop of an already competitive housing market. As insurance premiums rise, some buyers may be deterred from purchasing homes in high-risk areas, which could lead to a shift in demand and ultimately affect property values. This dynamic creates a complex interplay between insurance costs and real estate trends, further complicating the recovery process for communities affected by wildfires.
Furthermore, the situation is exacerbated by the fact that many insurers are opting to withdraw from high-risk markets altogether. This trend not only limits options for consumers but also raises concerns about the overall stability of the insurance market in California. As companies exit these markets, the remaining insurers may be left with a smaller pool of policyholders, which could lead to increased competition for coverage and, consequently, higher premiums. This cycle of rising costs and limited options poses significant challenges for residents and businesses alike.
In conclusion, the soaring wildfire losses in Los Angeles, now estimated at $20 billion, serve as a stark reminder of the evolving risks faced by insurers in California. As premiums rise in response to these challenges, homeowners and businesses must navigate a complex landscape marked by increased costs and limited options. The interplay between wildfire risks, insurance pricing, and the real estate market underscores the urgent need for innovative solutions to address the growing threat of wildfires and their far-reaching implications for the insurance industry and the communities it serves.
The Role of Climate Change in Wildfire Frequency
The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires in the United States, particularly in regions like California, has become a pressing concern for insurers and policymakers alike. As the recent catastrophic wildfires in Los Angeles have demonstrated, the financial implications of these natural disasters can be staggering, with losses soaring to an estimated $20 billion. This alarming trend can be largely attributed to the multifaceted impacts of climate change, which has altered weather patterns and created conditions conducive to the rapid spread of wildfires.
To understand the role of climate change in wildfire frequency, it is essential to consider the interplay between rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and shifting precipitation patterns. Over the past few decades, average temperatures in California have risen significantly, leading to hotter and drier conditions. These changes have not only increased the likelihood of wildfires but have also extended the wildfire season, allowing fires to ignite and spread more easily. As temperatures continue to climb, the window of vulnerability for wildfires expands, creating a persistent threat to both natural ecosystems and human settlements.
Moreover, the phenomenon of prolonged drought exacerbates the situation. Drought conditions dry out vegetation, turning it into highly flammable fuel for wildfires. In California, the combination of higher temperatures and reduced rainfall has resulted in severe droughts that have persisted for years, creating an environment ripe for wildfires. Consequently, as vegetation becomes increasingly desiccated, the risk of ignition rises, leading to more frequent and intense fire events. This cycle of drought and fire is further intensified by climate change, which is expected to continue influencing weather patterns in the region.
In addition to temperature and moisture changes, climate change also contributes to the increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as strong winds and lightning storms, which can ignite wildfires. For instance, Santa Ana winds in Southern California can propel flames rapidly, allowing fires to spread uncontrollably. These winds, coupled with dry conditions, create a perfect storm for wildfire outbreaks. As climate change continues to alter atmospheric conditions, the likelihood of such extreme weather events is expected to rise, further complicating efforts to manage and mitigate wildfire risks.
The implications of these changes extend beyond environmental concerns; they pose significant challenges for the insurance industry. As losses from wildfires escalate, insurers are faced with the daunting task of recalibrating their risk models to account for the increasing frequency and severity of these events. Traditional actuarial methods may no longer suffice, as they often rely on historical data that does not fully capture the rapid changes brought about by climate change. Consequently, insurers may need to raise premiums, limit coverage, or even withdraw from high-risk markets altogether, leaving many homeowners and businesses vulnerable.
In conclusion, the role of climate change in the frequency and intensity of wildfires is undeniable. As rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and extreme weather events converge, the risk of catastrophic wildfires continues to grow. This evolving landscape not only poses significant challenges for the environment but also places immense pressure on the insurance industry. As the recent losses in Los Angeles illustrate, the financial ramifications of these changes are profound, necessitating a reevaluation of risk management strategies and a concerted effort to address the underlying causes of climate change. Without proactive measures, the cycle of destruction wrought by wildfires is likely to persist, with far-reaching consequences for communities and insurers alike.
Policyholder Responses to Increased Wildfire Risks
As the frequency and intensity of wildfires continue to escalate, particularly in regions like Los Angeles, policyholders are increasingly confronted with the harsh realities of heightened wildfire risks. The recent surge in losses, which have soared to an alarming $20 billion, has prompted a significant shift in how individuals and businesses approach their insurance policies. In light of these developments, many policyholders are reassessing their coverage options, seeking to better protect themselves against the devastating impacts of wildfires.
One of the most immediate responses from policyholders has been to scrutinize their existing insurance policies. With the understanding that traditional homeowners’ insurance may not adequately cover the extensive damages caused by wildfires, many individuals are exploring additional coverage options. This includes specialized wildfire insurance, which is designed to address the unique risks associated with these catastrophic events. By seeking out policies that offer more comprehensive protection, policyholders aim to mitigate potential financial losses and ensure that they are not left vulnerable in the face of future disasters.
Moreover, as awareness of wildfire risks grows, policyholders are increasingly engaging in proactive measures to safeguard their properties. This includes implementing fire-resistant landscaping, creating defensible space around homes, and investing in fire-resistant building materials. Such actions not only enhance the safety of their properties but also serve as a signal to insurers that they are taking steps to reduce risk. In turn, this proactive approach may lead to more favorable insurance premiums, as insurers often reward policyholders who demonstrate a commitment to risk reduction.
In addition to these practical measures, many policyholders are also advocating for changes within the insurance industry itself. As losses mount, there is a growing call for insurers to develop more transparent and equitable pricing models that reflect the true risks associated with wildfire-prone areas. Policyholders are increasingly vocal about their concerns regarding rising premiums and the potential for coverage to be denied in the wake of a disaster. This advocacy is crucial, as it encourages insurers to reevaluate their practices and consider the long-term implications of their policies on communities at risk.
Furthermore, the emotional toll of wildfires cannot be overlooked. Many policyholders are grappling with the psychological impact of living in a constant state of uncertainty regarding their homes and livelihoods. This has led to a heightened demand for support services that address not only the financial aspects of recovery but also the emotional and mental health needs of those affected. Insurers are beginning to recognize the importance of providing comprehensive support to policyholders, which may include access to counseling services and community resources aimed at fostering resilience in the face of adversity.
As the landscape of wildfire risks continues to evolve, it is clear that policyholders are adapting in response to the challenges they face. By taking proactive steps to enhance their coverage, advocating for fair insurance practices, and seeking support for their emotional well-being, individuals and businesses are striving to navigate the complexities of an increasingly perilous environment. Ultimately, the collective response of policyholders will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of insurance in wildfire-prone areas, as they seek to balance the need for protection with the realities of an ever-changing climate. In this context, the dialogue between policyholders and insurers will be essential in fostering a more resilient approach to wildfire risk management.
Regulatory Changes for Insurers Post-Wildfire
In the wake of the devastating wildfires that swept through Los Angeles, resulting in staggering losses estimated at $20 billion, the insurance industry is grappling with the implications of these catastrophic events. As the frequency and intensity of wildfires continue to escalate, driven by climate change and urban expansion into fire-prone areas, regulatory changes are becoming increasingly necessary to ensure the stability and sustainability of the insurance market. These changes are not only a response to the immediate financial impact on insurers but also a proactive measure to address the long-term challenges posed by such natural disasters.
One of the primary regulatory changes being considered involves the reevaluation of risk assessment models used by insurers. Traditionally, these models have relied on historical data to predict future losses. However, the unprecedented nature of recent wildfires has highlighted the inadequacy of these models in accurately forecasting risks associated with climate change. Consequently, regulators are urging insurers to adopt more dynamic and comprehensive risk assessment methodologies that incorporate real-time data and predictive analytics. By doing so, insurers can better understand the evolving landscape of wildfire risks and adjust their underwriting practices accordingly.
Moreover, there is a growing consensus among regulators that insurers must enhance their transparency regarding coverage options and exclusions related to wildfire damage. Many policyholders have found themselves underinsured or unaware of the limitations of their coverage when disaster strikes. To address this issue, regulatory bodies are advocating for clearer communication from insurers about the terms of policies, including specific provisions related to wildfires. This initiative aims to empower consumers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about their insurance needs, ultimately fostering a more resilient community in the face of future wildfires.
In addition to improving risk assessment and transparency, regulators are also exploring the establishment of state-backed insurance pools. These pools would serve as a safety net for insurers facing overwhelming claims from catastrophic events like wildfires. By distributing the financial burden across a larger pool of resources, insurers can mitigate the risk of insolvency while ensuring that policyholders receive timely compensation for their losses. This approach not only stabilizes the insurance market but also encourages insurers to continue offering coverage in high-risk areas, which is crucial for maintaining the availability of insurance in regions prone to wildfires.
Furthermore, regulatory changes are likely to include incentives for insurers to invest in preventive measures and community resilience initiatives. By promoting programs that encourage property owners to implement fire-resistant landscaping, create defensible space around homes, and adopt building codes designed to withstand wildfires, regulators can help reduce the overall risk of loss. Insurers that actively support these initiatives may be rewarded with lower claims costs and, consequently, more favorable regulatory treatment.
As the insurance industry navigates the aftermath of the Los Angeles wildfires, it is clear that regulatory changes will play a pivotal role in shaping its future. By adopting more sophisticated risk assessment models, enhancing transparency, establishing state-backed insurance pools, and incentivizing preventive measures, regulators can help create a more resilient insurance landscape. Ultimately, these changes aim not only to protect insurers from the financial fallout of catastrophic events but also to safeguard communities and ensure that individuals have access to the coverage they need in an increasingly uncertain world. The path forward will require collaboration between regulators, insurers, and communities, as they work together to adapt to the realities of a changing climate and its impact on the insurance market.
Strategies for Insurers to Mitigate Future Losses
As the recent wildfires in Los Angeles have underscored the vulnerability of the insurance industry to natural disasters, insurers are compelled to reassess their strategies to mitigate future losses. The staggering $20 billion in losses from these wildfires serves as a wake-up call, prompting insurers to explore innovative approaches to risk management and loss prevention. One of the primary strategies involves enhancing data analytics capabilities. By leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, insurers can better predict and assess risks associated with wildfires. These tools enable companies to analyze vast amounts of data, including historical weather patterns, vegetation types, and urban development trends, allowing for more accurate risk modeling and pricing.
In addition to improving data analytics, insurers must also prioritize collaboration with local governments and communities. By engaging in partnerships, insurers can contribute to the development of more resilient infrastructure and land-use planning. For instance, investing in firebreaks, controlled burns, and vegetation management can significantly reduce the risk of wildfires spreading to residential areas. Furthermore, insurers can support community education initiatives that promote fire safety and preparedness, empowering residents to take proactive measures to protect their properties. This collaborative approach not only helps mitigate losses but also fosters a sense of shared responsibility among stakeholders.
Moreover, insurers should consider diversifying their coverage options to address the unique challenges posed by wildfires. Traditional homeowners’ insurance policies may not adequately cover the full extent of wildfire-related damages. Therefore, insurers can develop specialized products that cater to high-risk areas, offering tailored coverage that includes additional living expenses, debris removal, and rebuilding costs. By providing more comprehensive options, insurers can better meet the needs of policyholders while also managing their own risk exposure.
Another critical strategy involves investing in technology that enhances real-time monitoring and response capabilities. Drones and satellite imagery can be utilized to assess wildfire risks and monitor affected areas, enabling insurers to respond more swiftly to claims and damage assessments. This proactive approach not only streamlines the claims process but also allows insurers to gather valuable data that can inform future underwriting decisions. By staying ahead of potential disasters, insurers can minimize their financial exposure and improve customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, insurers must advocate for and support legislative measures aimed at reducing wildfire risks. This includes promoting policies that encourage sustainable land management practices and stricter building codes in fire-prone areas. By aligning their interests with public policy initiatives, insurers can play a pivotal role in shaping a more resilient environment, ultimately leading to reduced losses and a more stable insurance market.
In conclusion, the recent wildfire losses in Los Angeles highlight the urgent need for insurers to adopt multifaceted strategies to mitigate future risks. By enhancing data analytics, fostering community collaboration, diversifying coverage options, investing in technology, and supporting legislative measures, insurers can better navigate the challenges posed by natural disasters. As the frequency and intensity of wildfires continue to rise, these proactive measures will be essential in safeguarding both the financial stability of insurers and the well-being of the communities they serve. Through a concerted effort to innovate and adapt, the insurance industry can emerge stronger and more resilient in the face of an increasingly unpredictable climate.
Community Resilience and Insurance Solutions After Wildfires
The recent surge in wildfire losses, particularly highlighted by the staggering $20 billion in damages from the Los Angeles wildfires, has underscored the urgent need for enhanced community resilience and innovative insurance solutions. As the frequency and intensity of wildfires continue to escalate, driven by climate change and urban expansion into fire-prone areas, communities are increasingly recognizing the importance of proactive measures to mitigate risks. This recognition is not merely a response to immediate threats but a strategic approach to fostering long-term sustainability and safety.
In the wake of such devastating losses, it becomes imperative for communities to invest in resilience-building initiatives. These initiatives can take various forms, including improved land management practices, the establishment of defensible spaces around properties, and the implementation of community-wide fire prevention programs. By prioritizing these strategies, communities can significantly reduce their vulnerability to wildfires, thereby protecting lives and property. Furthermore, engaging local residents in these efforts fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, which is crucial for the success of any resilience strategy.
Moreover, the role of insurance in this context cannot be overstated. Traditional insurance models often struggle to keep pace with the evolving landscape of wildfire risks. As losses mount, insurers face increasing pressure to adjust their policies and pricing structures. This situation creates a pressing need for innovative insurance solutions that not only provide coverage but also incentivize risk-reduction behaviors among policyholders. For instance, insurers can offer premium discounts for homeowners who implement fire-resistant landscaping or invest in fireproof building materials. Such incentives not only encourage proactive measures but also align the interests of insurers and policyholders in reducing overall risk.
In addition to individual policyholder initiatives, community-wide insurance programs can play a pivotal role in enhancing resilience. These programs can pool resources and spread risk across a larger base, making coverage more affordable and accessible for residents in high-risk areas. By collaborating with local governments and community organizations, insurers can develop tailored solutions that address the unique challenges faced by specific regions. This collaborative approach not only strengthens community ties but also fosters a shared commitment to resilience.
Furthermore, technology is emerging as a powerful ally in the quest for improved wildfire resilience and insurance solutions. Advanced data analytics and modeling tools enable insurers to better assess risk and develop more accurate pricing models. Additionally, real-time monitoring systems can provide critical information during wildfire events, allowing for more effective response strategies. By harnessing these technological advancements, insurers can enhance their ability to predict and respond to wildfire risks, ultimately benefiting both their bottom line and the communities they serve.
As the landscape of wildfire risk continues to evolve, it is clear that a multifaceted approach is necessary to build resilience and develop effective insurance solutions. Communities must prioritize proactive measures that reduce vulnerability, while insurers must adapt their models to reflect the realities of a changing environment. By fostering collaboration between residents, local governments, and insurance providers, it is possible to create a more resilient future in the face of increasing wildfire threats. Ultimately, the lessons learned from the recent Los Angeles wildfires can serve as a catalyst for change, prompting a collective commitment to safeguarding lives and properties against the devastating impacts of wildfires.
Q&A
1. **What is the estimated loss from the Los Angeles wildfires?**
– The estimated loss from the Los Angeles wildfires is $20 billion.
2. **How are US insurers affected by the wildfire losses?**
– US insurers are facing significant financial setbacks due to the high costs of claims resulting from the wildfires.
3. **What factors contribute to the rising costs of wildfire damages?**
– Factors include increased property values, more extensive damage due to urban development in fire-prone areas, and climate change leading to more severe wildfires.
4. **What impact do these losses have on insurance premiums?**
– The losses are likely to lead to higher insurance premiums for homeowners in wildfire-prone areas.
5. **Are there any specific insurers that are particularly affected?**
– While specific insurers may vary, many large national and regional insurers are likely to be impacted due to their exposure in California.
6. **What measures are insurers taking in response to the wildfire risks?**
– Insurers may implement stricter underwriting guidelines, increase premiums, or limit coverage in high-risk areas.
7. **How does this situation reflect broader trends in the insurance industry?**
– This situation highlights the growing challenges insurers face due to climate change and natural disasters, prompting a reevaluation of risk assessment and pricing strategies.
Conclusion
The soaring losses from the Los Angeles wildfires, reaching $20 billion, represent a significant setback for U.S. insurers, highlighting the increasing financial risks associated with climate change and natural disasters. This situation underscores the urgent need for the insurance industry to adapt its models and strategies to better manage and mitigate the impacts of such catastrophic events, while also prompting discussions on policy reforms and community resilience initiatives.